什麼是同步、非同步?
同步(synchronous)的意思是指一次只能進行一件事、一件任務,非同步或稱異步(asynchronous)的意思則是不用等上一任務完成再執行。只看名字容易搞混,但如果想成是同一個步道和不同步道,會比較好理解。同步道因為只有一個步道所以一次只能執行一項任務,而不同步道可以多個任務一起執行。
JavaScript 如何實現非同步?
JavaScript 這種編程語言,我們稱之為腳本(script)、直譯式語言,可以寫在 HTML 中,在頁面加載的時候會自動執行。只要瀏覽器或伺服器有搭載 JavaScript Engine 在環境中,就可以執行 JavaScript。
Scripts are provided and executed as a plain text. They don’t meed a special preparation or a compilation to run. In this aspect, JavaScript is very different from another language called JAVA. JAVA needs to be compiled into machine code.
在使用 C、C++、JAVA 之類傳統語言,執行前需要先編譯,這可以為程式碼產生機器的有效表達方式,通常可以優化執行時期的效能。早期的 JavaScript 因為直譯式語言的命令稿語言設計而在性能上表現不佳,但因其對 web 的發展重要性日益增長,許多企業資源和優秀人才的投入,現在既可收命令稿語言的便利性又可享有編譯式語言的性能。
直譯式和編譯式程式語言的差別在於:直譯式語言需要經過 直譯器 interpreter 逐行轉換,且它是在執行時才被直譯成執行碼,效能一部分取決於直譯器的速度,直譯式語言多為動態語言(dynamic language),具有靈活的型別處理,在執行時才動態生成等彈性。直譯式語言仰賴一個執行環境(execution context)語言可用的功能由這個執行環境提供。
編譯式語言經由 編譯器 compiler 轉換成目的碼(object code)再由連結器(linker)轉換成可執行的二進位碼(byte code)。編譯式語言多為靜態語言(static langauge)有事先定義的型別、型別檢查及高效能執行速度等特性。
由 Google 開發(2008)的 open source Engine:V8 是實現 JavaScript 在瀏覽器環境非同步執行的最佳功臣;在 V8 之前的 Engine 都太慢了,Google 為了讓 JavaScript 能夠在瀏覽器上跑得更快,開發了以 C++ 語言寫成的 V8。V8 將 JavaScript 在執行前編譯成了機器碼(machine code,是電腦的CPU可直接解讀的資料);而位元組碼(bytecode,是為了實現特定軟體運行、軟體環境、與硬體環境無關)或是解釋執行它,並使用了 inline-caching 行內快取等方法,提升效能,使其速度能夠媲美二進制編譯。
每個瀏覽器(Google Chrome, FireFox, IE, Safari)都有自己的 JavaScript Engine implementation and all of them have a JavaScript runtime that provide web APIs. 這些 web APIs 是種應用程式,負責許多瀏覽器運作所需的操作,包括 send HTTP Request, listen to DOM events, delay execution by using setTimeout and setInterval, caching, database storage…etc. 也可以儲存資料、暫存在瀏覽器。其他 Engine 還有 Spider Monkey(used by FireFox)以及 Chakra(used by IE) 等。
JavaScript is a single threaded language that can be non-blocking.
JavaScript 是單一執行緒(single threaded execution)的程式語言,意思是一次只能處理一個需求(任務),所有的 line code 在執行堆疊(call stack)中記錄執行情況,每次只會執行一個程式碼片段(one thing at a time = one call stack)。
執行堆疊(call stack)會紀錄目前執行到程式的哪個部分,如果進入了某個 function,便會把這個 function 添加到堆疊的最上方,如果 function 執行了 return 便會把 function 從堆疊中抽離(pop off),在堆疊中的資料是遵守 first-in-last-out 的順序。
雖然 JavaScript 執行程式是同步的,逐一執行,但因為在瀏覽器環境中,還有 Rendering Engine 和 HTTP Request,所以整個網頁在執行過程中可以達到非同步的運作。
JavaScript Run-Time Environment?
JavaScript Run-Time Environment 就是指 JavaScript 的執行環境,下圖為執行環境的示意:
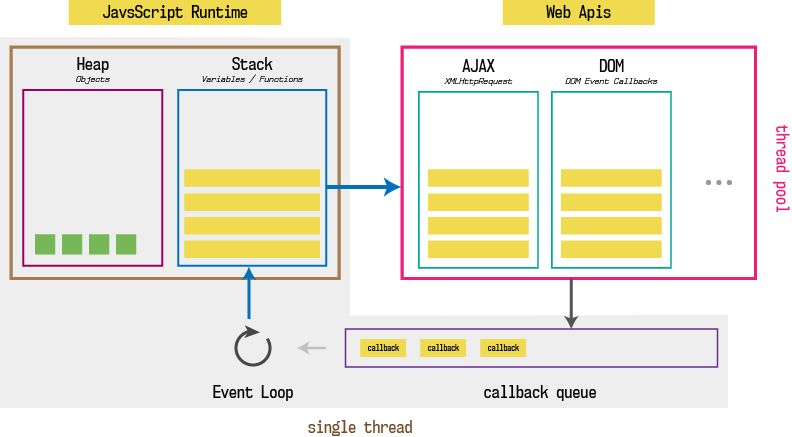
JavaScript 依靠這些機制運作執行:
- Memory Heap 記憶、儲存。 JavaScript automatically allocates memory when objects are created and frees it when they are not used anymore(Garbage Collection).
- Call Stack 執行堆疊,紀錄當前程序所在位置的數據結構,從最上方開始執行。
- Event Loop 事件循環,不斷檢查 Call Stack 是否為空的。
- Callback Queue 佇列,遵守 fisrt-in-first-out 的資料處理順序。
- Web APIs 由瀏覽器提供的應用程式,例如:fetch(), DOM events, setTimeout, setInterval…etc. These Web APIs are asynchronous. That means, you can instruct these APIs to do something in background and return data once done, meanwhile we can continue further execution of JavaScript code. While instructing these APIs to do something in background, we have to provide a callback function. Responsibility of callback function is to execute some JavaScript once Web API is done with it’s work.
在瀏覽器執行 JavaScript 時, call stack 會將不屬於 JavaScript 原生處理範圍的函式或程式碼,丟給 Web APIs 處理,再將處理結果丟到 Callback Queue,透過 Event Loop 不斷查詢是否 Call Stack is empty?如果沒有等待執行的程式碼,再將 Callback Queue 佇列中的第一項放到 Call Stack 中去執行。由於 Event Loop 運作的關係,瀏覽器的 JavaScript 可以同時執行多個需求,而不需要等待上個需求完成才進行下一個。
非同步的 JavaScript
以下介紹幾個在 JavaScript 中實現非同步操作的語法:
setTimeout() & setInterval()
setTimeout 和 setInterval 是由瀏覽器提供的 Web APIs,可以延遲任務執行時間,作為計時器使用。
ES6: Promise
為了解決 callback hell 的問題和串接 function 的需求,JavaScript 在 ES6 中加入了 Promise,Promise is saying that “hey, I am doing somthing and I promise to let you know when I have the result.” A promise is an object that may produce a single value some time in the future, either a resolved value, or a reason that it’s not resolved(rejected). Promise 讓非同步請求處理更容易,是一種非同步編程的解決方案。Promise object 是一個構造函數,需要用 new 語法來生成 promise 實例:
1 | const promise = new Promise( function(resolve, reject){ |
Promise 有三種狀態:pending、fulfilled、rejected,分別代表當前腳本任務的執行狀況。當 Promise 實例生成後,可以用 .then(function(){}, function(){}) 方法分別指定 fulfilled 和 rejected 狀態時的回調函數(callback function):
1 | promise.then( |
fetch() API
A fetch simply return a promise.
1 | fetch('url') |
fetch 實作基於 es6 promise,在 2015 年由 google 發佈,fetch 回傳的 promise 物件不會再有收到 response 但是 http status 呈現 404 或 500 的時後變成 rejected,只會在網路出現問題或是被阻止 request 時,狀態才會變成 rejected,其他都是 fulfilled。
由於 fetch 會返回一個 promise 所以可以使用 .then 來串接,避免撰寫 callback hell 程式碼,通常使用時會用 .catch 來捕捉 promise 發生的 error。
ES8: Async/Await
Async/Await is bulit on top of Promises. 目的是簡化使用 promise 的行為。我們可以使用 async ()=>{}來宣告一個非同步函式,這個非同步函式會返回一個 promise。 Every function that returns a promise can be considered as async function. async function 是不管怎樣都會回傳 Promise 的函式,雖然我們回傳的不是一個 Promise,但因為它是 async function 的關係,JS 會自動把它包成 Promise,所以可以使用 then:
1 | const foo = async () => { |
await 必須在 async function 裡面才能使用,await可以在所有 return a promise 的程式碼前使用,await 會等 promise 執行完,再執行下一行。await 也能夠把 Promise 回傳的值接起來,通常我們在呼叫 API(例如執行 fetch、axios)的時候就很好用:
1 | fetch('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users') |
改寫成 async function:
1 | async function fetchUsers() { |
使用 async/await 處理多個 非同步請求以及除錯,比使用 promise 的 then 鏈,更容易除錯:
這是使用 promise 和 try/catch 用法:
1 | function loadData() { |
這是使用 asyn/await 和 try/catch:
1 | async function loadData() { |
在錯誤發生時,如果是用 .then 返回的錯誤堆疊不提供錯誤發生在哪裡,不容易找到錯誤發生原因:
1 | function loadData() { |
使用 async/await 便可以逐行找到錯誤發生的地方:
1 | async function loadData() { |
JavaScript vs Node.js
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime bulit on Google chrome’s V8 engine. 2009 Ryan Doll decided it would be great to run it ouside the browser. So he created Node.js which is actually a C++ program. It’s an executable C++ program that provides JS runtime for us.
Node.js uses Google chrome’s V8 engine to provide JavaScript runtime but does not rely only on it’s event loop. It uses libuv library (written in c) to work along side V8 event loop to extend what can be done in background. Node follows same callback approach like Web APIs and works in similar fashion as the browser.
Node.js 的執行系統圖示:

If you compare browser diagram with above node diagram, you can see the similarities. The entire right section looks like Web API but it also contains event queue (callback queue/message queue) and the event loop. But V8, event queue and event loop runs on single thread while worker threads are responsible to provide asynchronous I/O operation. That’s why Node.js is said to have as non-blocking event driven asynchronous I/O architecture.
I/O 指 input/output,資訊處理系統與外部世界(使用者、另一個資訊處理系統)之間的通訊,包括輸入:接收訊號或資料;輸出:發送訊號或資料。任何資訊傳入或傳出 CPU/記憶體組合,例如通過磁盤驅動器讀取資料,就會被認為是 I/O。
Asynchronous Node.js
由 Node.js 建立的後端伺服器,可以使用 Express.js 框架來處理非同步請求的操作,Express.js 是一個基於 Node.js 平台,極簡、靈活的框架,擁有強大的特性可以幫助開放網頁應用。
使用 Express.js 就是調用各種中間件(middleware)來處理各種請求、管理路由,其本身也可以視為是一種中間件(middleware)。通過 Express.js 提供的執行函數調用對應的方法,比起直接在 Node.js 中寫處理程式,會更加方便和快捷。
Reference
How JavaScript works in browser and node?
Udemy course “Advanced JavaScript Concepts”
學習Express前,都會搞懂這幾個問題